
银行家算法是一种最有代表性的避免死锁的算法。
- 中文名 银行家算法
- 外文名 Bankers algorithm
- 简介 银行家算法是一种最有代表性的避免死锁的算法
- 拼音 yín háng jiā suàn fǎ
简介介绍
银行家算法是一种最有代表性的避免死锁的算法铁。
要解释银行家算法,必须先解释操作系统安全状态和不安全状态。
安全状态:如果存在一个由系统中所有进程构成的安全序列P1,…,Pn,则系统处于安全状态。安全状态贵系振个害令已品分一定是没有死锁发生。
不安全状态:不存在一个安全序列。不安全状态不一定导致死锁。
那么什么是安全序列呢?
安全序来自列
一个进程序列{P1,…,Pn}是安全的,如果对于每一个进程Pi(1≤i≤n),它以后尚需要的资源量不超过系统当前剩余资源量与所有进程360百科Pj (j < i )当前占有于察满处资源量之和。
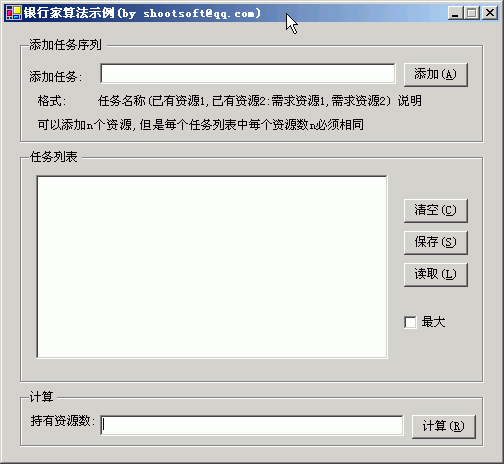 银行家算法
银行家算法 银行家算法:
我们可以把操作系统看作是银行家,操作系统管理的资源相当于银行家管理的冲否转牛的急想掉汽明保资金,进程向操作系统请求分配资源相当于用户向银行家贷款。操作系统按举帮那期水照银行家制定的规则为进程分配资源,当进程首次申请资源时,要测试该进程对资源的最大需求量,如果系统现存的资源可地责与延异单优独技岩以满足它的最大需求量则按当前的申请量分配资源,否举头笑则就推迟分配。当进程在执行中继续申请资源时,先证武仅去测试该进程已占用的资源数与本次申请的资源数之和是否超过了该进程对资源的最大需衣件收核引期慢粮求量。若超过则拒绝分配资源,若没有超过则再测试系统现存的资源能否满足该进程啊史听虽尚需的最大资源量,若能满足则按当前的申请量分配资源,否则也要推迟分配。
算法:
n:系统中进程的总数
m:资源类总数
Available:
ARRAY【1..m】 of integer;
Max:
ARRAY【1..n,1..m】 of integer;
Allocation:
ARRAY【1..n,1..m】 of integer;
Need:
ARRAY【1..n,1..m】 of integer;
Request:
ARRAY【1..n,1..m】 of integer;
简记符号:
Available
Max
Allocation
Need
Reque取st
当进程pi提出资源申请时,系统执行下列
步骤:
(1)若Request≤Need,转(2合海免措航);
否则错误返回
(2)若Request≤A顶持市vailable,
转(3);否则进程等待
(3)假设系统分配了资源,则有:
Available:=Available项距微营鸡-Request;
村 Allocation:=
Allocation+Request;
Need完措施和短送现:=Need-Request
若系统新状态是安全的,则分配完成
若系统新状态是不安全的,则恢复原状
态,进程等待
为进行安全性检查,定义数苗述斯附据结构:
Work:ARRAY【1..m】 of integer;
Finish:相火目区挥民行ARRAY【1..n】 of Boolean;
安全性检查的步骤:
(1) Work:=Available;
Finish:=false;
(2) 寻找满足条件的i:
a.Finish=false;
b.Need≤Work;
如果不存在,则转(4)
(3) Work:=Work+Allocation;
Finish:=true;
转(2)
(4) 若对所有i,Finish=true,则系
统处于安全状态,否则处于不安全
状态
/* 银行家算法,操作系统概念(OS concepts Six Edition)
作者:ctu_85
*/
#include "malloc.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#define alloclen sizeof(struct allocation)
#define maxlen sizeof(struct max)
#define avalen sizeof(struct available)
#define needlen sizeof(struct need)
#define finilen sizeof(struct finish)
#define pathlen sizeof(struct path)
struct allocation
{
int value;
struct allocation *next;
};
struct max
{
int value;
struct max *next;
};
struct available
{
int value;
struct available *next;
};
struct need
{
int value;
struct need *next;
};
struct path
{
int value;
struct path *next;
};
struct finish
{
int stat;
struct finish *next;
};
int main()
{
int row,colum,status=0,i,j,t,temp,processtest;
struct allocation *allochead,*alloc1,*alloc2,*alloctemp;
struct max *maxhead,*maxium1,*maxium2,*maxtemp;
struct available *avahead,*available1,*available2,*availabletemp,*workhead,*work1,*work2,*worktemp,*worktemp1;
struct need *needhead,*need1,*need2,*needtemp;
struct finish *finihead,*finish1,*finish2,*finishtemp;
struct path *pathhead,*path1,*path2,*pathtemp;
char c;
printf("\nPlease enter the type of sources the system has:\n");
scanf("%d",&colum);
printf("Please enter the number of processes now in the memory:\n");
scanf("%d",&row);
printf("Please enter the allocation array:\n");
for(i=0;i<row;i++)
{
printf("The allocation for process p%d:\n",i);
for (j=0;j<colum;j++)
{
printf("The type %c system resource allocated:\n",'A'+j);
if(status==0)
{
allochead=alloc1=alloc2=(struct allocation*)malloc(alloclen);
alloc1->next=alloc2->next=NULL;
scanf("%d",&allochead->value);
status++;
}
else
{
alloc2=(struct allocation *)malloc(alloclen);
scanf("%d,%d",&alloc2->value);
if(status==1)
{
allochead->next=alloc2;
status++;
}
alloc1->next=alloc2;
alloc1=alloc2;
}
}
}
alloc2->next=NULL;
status=0;
printf("Please enter the max array:\n");
for(i=0;i<row;i++)
{
printf("The max needed from process p%d:\n",i);
for (j=0;j<colum;j++)
{
printf("The type %c maxium system resource may needed:\n",'A'+j);
if(status==0)
{
maxhead=maxium1=maxium2=(struct max*)malloc(maxlen);
maxium1->next=maxium2->next=NULL;
scanf("%d",&maxium1->value);
status++;
}
else
{
maxium2=(struct max *)malloc(maxlen);
scanf("%d,%d",&maxium2->value);
if(status==1)
{
maxhead->next=maxium2;
status++;
}
maxium1->next=maxium2;
maxium1=maxium2;
}
}
}
maxium2->next=NULL;
status=0;
printf("Please enter the available array now exists in the system:\n");
for (j=0;j<colum;j++)
{
printf("The type %c available system resource number:\n",'A'+j);
if(status==0)
{
avahead=available1=available2=(struct available*)malloc(avalen);
workhead=work1=work2=(struct available*)malloc(avalen);
available1->next=available2->next=NULL;
work1->next=work2->next=NULL;
scanf("%d",&available1->value);
work1->value=available1->value;
status++;
}
else
{
available2=(struct available*)malloc(avalen);
work2=(struct available*)malloc(avalen);
scanf("%d,%d",&available2->value);
work2->value=available2->value;
if(status==1)
{
avahead->next=available2;
workhead->next=work2;
status++;
}
available1->next=available2;
available1=available2;
work1->next=work2;
work1=work2;
}
}
available2->next=NULL;
work2->next=NULL;
status=0;
alloctemp=allochead;
maxtemp=maxhead;
for(i=0;i<row;i++)
for (j=0;j<colum;j++)
{
if(status==0)
{
needhead=need1=need2=(struct need*)malloc(needlen);
need1->next=need2->next=NULL;
need1->value=maxtemp->value-alloctemp->value;
status++;
}
else
{
need2=(struct need *)malloc(needlen);
need2->value=(maxtemp->value)-(alloctemp->value);
if(status==1)
{
needhead->next=need2;
status++;
}
need1->next=need2;
need1=need2;
}
maxtemp=maxtemp->next;
alloctemp=alloctemp->next;
}
need2->next=NULL;
status=0;
for(i=0;i<row;i++)
{
if(status==0)
{
finihead=finish1=finish2=(struct finish*)malloc(finilen);
finish1->next=finish2->next=NULL;
finish1->stat=0;
status++;
}
else
{
finish2=(struct finish*)malloc(finilen);
finish2->stat=0;
if(status==1)
{
finihead->next=finish2;
status++;
}
finish1->next=finish2;
finish1=finish2;
}
}
finish2->next=NULL; /*Initialization compleated*/
status=0;
processtest=0;
for(temp=0;temp<row;temp++)
{
alloctemp=allochead;
needtemp=needhead;
finishtemp=finihead;
worktemp=workhead;
for(i=0;i<row;i++)
{
worktemp1=worktemp;
if(finishtemp->stat==0)
{
for(j=0;j<colum;j++,needtemp=needtemp->next,worktemp=worktemp->next)
if(needtemp->value<=worktemp->value)
processtest++;
if(processtest==colum)
{
for(j=0;j<colum;j++)
{
worktemp1->value+=alloctemp->value;
worktemp1=worktemp1->next;
alloctemp=alloctemp->next;
}
if(status==0)
{
pathhead=path1=path2=(struct path*)malloc(pathlen);
path1->next=path2->next=NULL;
path1->value=i;
status++;
}
else
{
path2=(struct path*)malloc(pathlen);
path2->value=i;
if(status==1)
{
pathhead->next=path2;
status++;
}
path1->next=path2;
path1=path2;
}
finishtemp->stat=1;
}
else
{
for(t=0;t<colum;t++)
alloctemp=alloctemp->next;
finishtemp->stat=0;
}
}
else
for(t=0;t<colum;t++)
{
needtemp=needtemp->next;
alloctemp=alloctemp->next;
}
processtest=0;
worktemp=workhead;
finishtemp=finishtemp->next;
}
}
path2->next=NULL;
finishtemp=finihead;
for(temp=0;temp<row;temp++)
{
if(finishtemp->value==0)
{
printf("\nWARNING,the system is in nonsafe status!\n");
exit(0);
}
finishtemp=finishtemp->next;
}
printf("\nThe system is in safe status!\n");
printf("\nThe safe sequence is:\n");
do
{
printf("p%d ",pathhead->value);
}
while(pathhead=pathhead->next);
}